CLIMATE CHANGE FACTS
What is climate change? Why is climate change happening? Why does all this matter? Plus how to know who and what to believe when there is often conflicting information
What is Climate Change?
The United Nations describe climate change as:
"long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns. Such shifts can be natural, due to changes in the sun’s activity or large volcanic eruptions. But since the 1800s, human activities have been the main driver of climate change, primarily due to the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas."
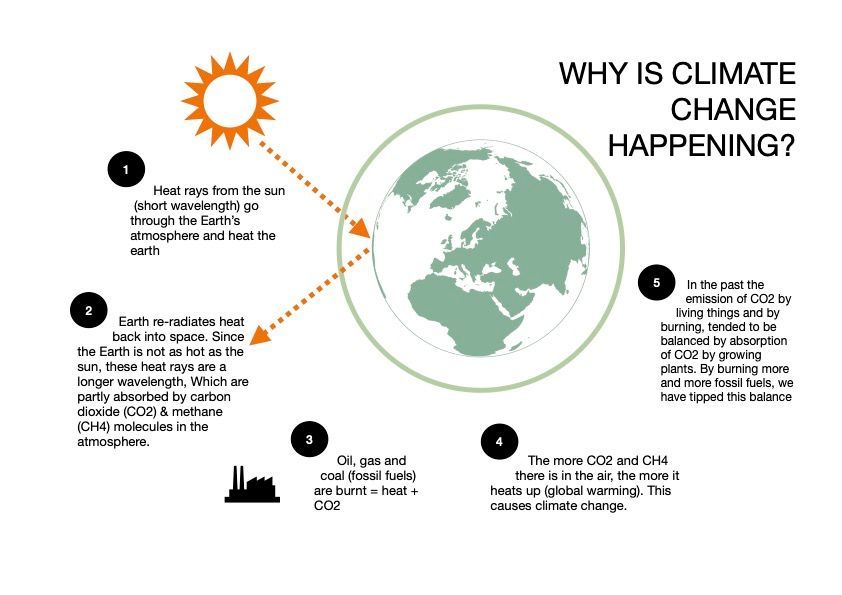
There is a large scientific consensus that human activities are the main cause of current climate change. This consensus is supported by evidence from the atmosphere, oceans, cryosphere, and biosphere.The diagram below illustrates how climate change occurs and how our activities are associated with this change.
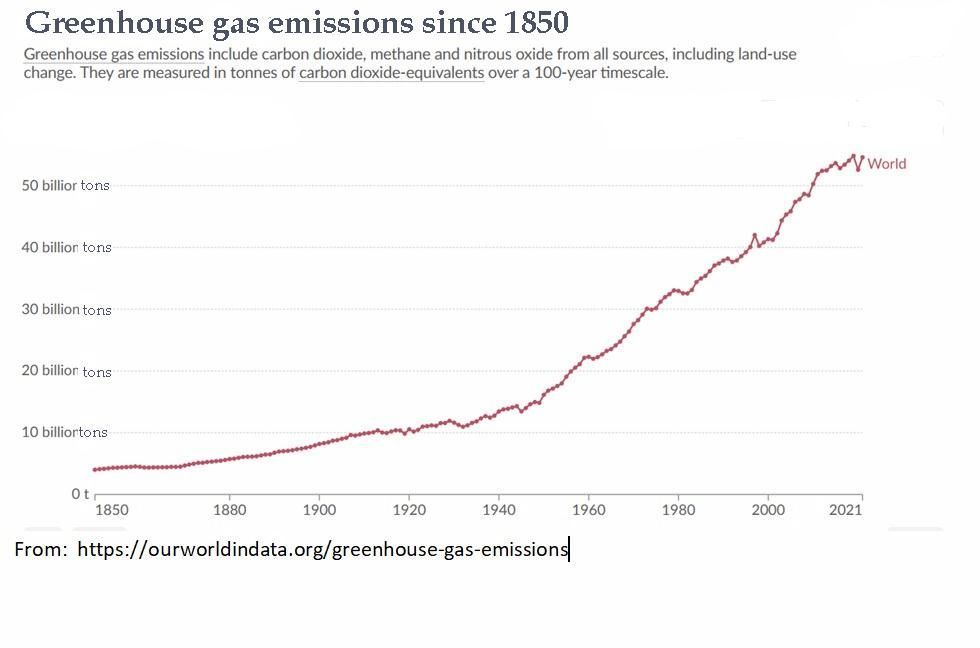
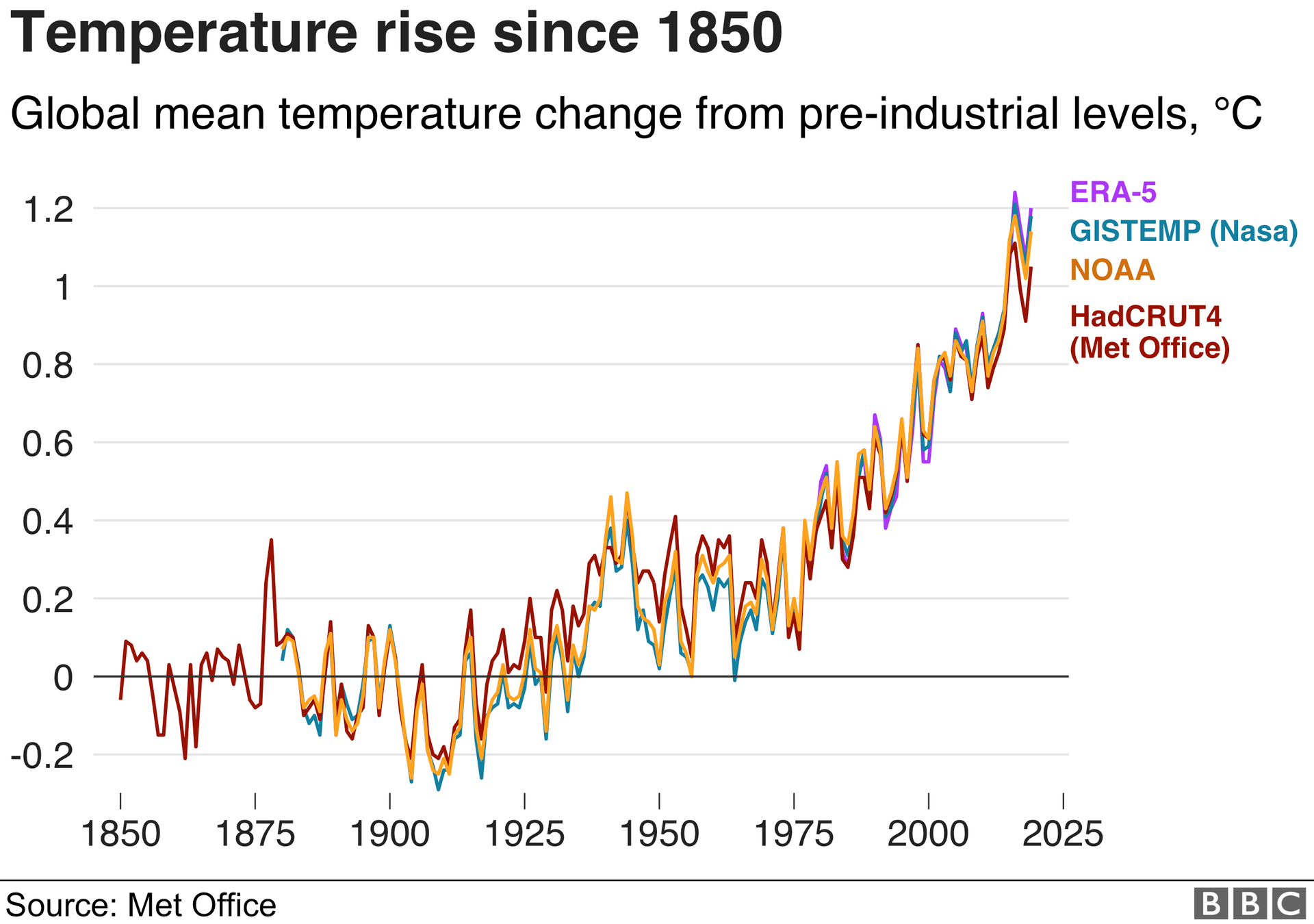
The two graphs below show how greenhouse gas emissions (left) and global mean temperatures (right) have increased since 1850. The shapes of the graphs are almost identical
CLIMATE CHANGE DENIERS AND MISINFORMATION
The fossil fuel industry spends a lot of money obstructing efforts to mitigate Climate Change, by sowing doubt about the evidence that it is due to human activity. One organisation is The Global Warming Policy Foundation (GWPF), set up in 2008 by Lord Lawson (former Conservative Chancellor). They want to protect the profits they make from the fossil fuel industry (just as the Tobacco industry denied the link between smoking and cancer for 30 years, investing millions in sowing self-interested misinformation).
For an example see the 2021 lecture delivered by Professor Koonin for the GWPF, funded by Fossil Fuel Companies, entitled ''Unsettled'' (2021 Annual GWPF Lecture | Steven E Koonin | Unsettled)
For a scientific rebuttal of the arguments in this lecture see ‘’Debunking Denial’’ by Steven Vigdor and Tim Londergan Emeritus Professors of Indiana University.
WHY WE CAN TRUST THE SCIENCE
An overwhelming 99% of scientists agree that climate change is caused by human greenhouse gas emissions. Scientists employ ‘Scientific Method’ where experiments or observations are conducted and statistically analysed. Their methodology and results are described in detail so that others could repeat their work and independently verify the results. Before publication, their work is ‘peer-reviewed’ (checked and questioned by other scientists). This method ensures confidence in the results produced.


